Is It Possible To End China’s Control of The Global Supply Chain?

Any broader effort to restructure supply chains is little more than wishful thinking so far, analysts say
The trade war amplified calls in the US and elsewhere for reducing dependence on China for strategic goods. Now, the pandemic has politicians vowing to take action.
The Trump administration has talked about bringing supply chains home from China, and even publicly floated the need for a group of friendly nations in Asia that could help produce essential goods. President Donald Trump last month even said the U.S. would “save $500 billion” if it cut off ties with China.
But interviews with nearly a dozen government officials and analysts in the Asia-Pacific region show that any broader effort to restructure supply chains is little more than wishful thinking so far. While governments are pushing to win investments, such as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co.’s planned state-of-the-art semiconductor factory in the U.S., it won’t be simple to dismantle an entrenched system when many companies are struggling to survive.
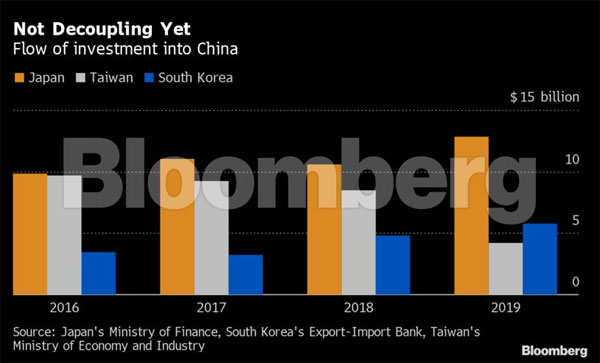
More likely is that the virus will accelerate a change that was already driven by market forces as rising wages and costs in China over the past decade caused an exodus of lower-value manufacturing, much of it to Southeast Asia. That’s despite the desire from some in the Trump administration to start decoupling the world’s biggest economies as the U.S. and China spar over everything from the virus to 5G networks to Hong Kong.
Not Decoupling Yet
“The rhetoric meets the reality, which is that many firms have supply chains set up the way they do for very sensible reasons,” said Deborah Elms of the Asian Trade Centre, which has seen an increase of companies looking for advice on reorganizing to increase competitiveness. “Coming out of COVID, it’s going to be even harder to move supply chains because your cash flow is low, your staff are working from home or coming slowly back into the office, and the business climate has shifted.”
While the world trade network mostly held up well amid rolling lockdowns as COVID-19 spread, the economic cost fuelled calls among politicians for greater self-sufficiency and alternatives to China. U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo, whose department announced an Economic Security Strategy last year, in April named Australia, New Zealand, Japan, India, and South Korea as countries that the U.S. has been talking to on supply chains.
A key plank of the State Department’s new Economic Security Strategy is expanding and diversifying supply chains that protect “people in the free world,” according to Keith Krach, a State Department official who leads efforts to develop international policies related to economic growth.
Krach said in April a so-called “Economic Prosperity Network” of like-minded allies would be built for critical products.
‘China Plus One’
Industries would include pharmaceuticals, medical devices, semiconductors, automotive, aerospace, textiles and chemicals, among others.
But the idea right now appears to lack any firm foundation. The State Department doesn’t have jurisdiction over trade, and officials in other Asian countries said no formal talks were taking place. A person close to the administration said Krach is prone to pushing grand ideas publicly that haven’t yet become policy.
Still, other governments are moving on their own to shift production away from China -- especially since the COVID disruptions. This includes Taiwan and Japan, which were among the biggest investors in China’s manufacturing capacity in the early days.
“Many companies have already begun adopting a ‘China plus one’ manufacturing hub strategy since the U.S.-China trade war began in 2018, with Vietnam having been a clear beneficiary,” said Anwita Basu, head of Asia country risk research at Fitch Solutions. While the pandemic will give that another push, “shifts away from China will be slow as that country still boasts an annual manufacturing output that is so large that even a group of countries would struggle to absorb a fraction of it.”
In 2019, Taiwanese officials encouraged the island’s firms to build a “non-red supply chain” outside of China, passing a law that promised rent assistance, cheap finance, tax breaks and simplified administration for investments in Taiwan. The move helped the island’s economy weather the trade war last year and led to more than NT$1 trillion ($33.5 billion) pledged or invested domestically, and more overseas.
Japan recently started down the same path, with Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s government budgeting about 220 billion yen ($2 billion) for companies shifting production back home and 23.5 billion yen for those seeking to move production to other countries.
“Everyone agrees we really have to reconsider the sustainability of supply chains,” Hiroaki Nakanishi, chairman of Hitachi Ltd. and head of Japan’s biggest business lobby Keidanren, said on television last month. “It’s unrealistic to suddenly return all production to Japan. But if we are totally reliant on one specific country and they have a lockdown, there will be huge consequences.”
South Korea has similar plans as part of its economic blueprint for the rest of the year, announced earlier this month. The government said it will provide tax incentives, ease investment-related regulations and expand financial support for companies that ‘U-Turn.’ Yet, it hasn’t said how much money will be earmarked for the entire support program.
For all that, China retains some key advantages. Last year 38% of Taiwan’s $11 billion of overseas investment still went to the mainland, as did 10% of Japan’s -- despite increased investments in Southeast Asia over the past few decades due to periodic bouts of anti-Japanese rioting in China.
Young Liu, chairman of Taiwan-based Hon Hai Precision Industry, whose Foxconn unit manufactures iPhone in plants in China, said in mid-May that it’s difficult to move assembly of mobile devices to the U.S due to the sheer number of workers needed.
“China remains unmatched as a manufacturing site given its numbers of skilled workers, deep supplier networks and the government’s credible public support for manufacturers and provision of reliable infrastructure,” wrote Gavekal Dragonomics analyst Dan Wang in a report in April.
Even if companies find economic alternatives to Chinese factories, or bow to political pressure to increase production in their home markets, there’s another reason why production inside China continues to make sense: the vast and growing Chinese domestic market.
Tesla, Honeywell
Tesla Inc. is now producing cars there for what is now the world’s largest auto market, and last month Chinese Premier Li Keqiang sent Honeywell International Inc. a letter welcoming its new investment in Wuhan, the city where the coronavirus outbreak started. He and other Chinese officials have touted continued economic cooperation with the U.S. and vowed to implement a “phase one” trade deal with the U.S. reached in January.
“The formation and development of global industrial and supply chains are determined by market forces and companies’ choices,” Chinese foreign ministry spokesman Geng Shuang said in March. “As such, it is unrealistic and insensible to try to sever them or even trumpet ‘shifting’ or ‘decoupling’ theories as they run counter to economic law.”
For all the talk of dependence on China, the pandemic showed that other nations could quickly adapt to meet the need for critical supplies when China’s lockdown halted deliveries of protective clothing, ventilators and medical supplies. Vietnam rapidly ramped up production of face masks, exporting more than 415 million in four months, while the U.S. pushed automakers and other manufacturers to retool plants to make respirators and other critical supplies.
Over the long term, however, there are questions of whether those models are sustainable -- and who will pay for new plants outside China.
Waving A Wand
A May 14 executive order from Trump allows the U.S. International Development Finance Corp., America’s development bank for emerging markets, to partner with the Department of Defence in the U.S. to lend money to American companies looking to build out supply chains for critical goods such as ventilators and generic drugs.
But with governments already having to fund trillions of dollars in bailout packages for existing businesses and companies going bust in droves, finding the extra capital to restructure global supply chains is a tall order. Andrew Hastie, an Australian lawmaker and chair of the nation’s security and intelligence committee, called in a recent essay for “time limited tax incentives” to build national self-reliance in key pharmaceuticals, medical supplies and other critical goods.
In the end, the biggest force diluting China’s position in the global supply chain will likely be the long, slow evolution of global trade, as companies see opportunities that arise from new markets, new technologies and changing patterns of wealth. Why would a firm “say to their staff and their shareholders we have opted for political reasons to change the way that we do things,” said Elms, whose organization helps governments formulate trade policy.
“The numbers have to make sense,” she said. “The structure that you have is based on millions of individual company decisions. It’s not so easy to wave a wand and say: Make it So!”



No comments:
Post a Comment